In September every year we celebrate Chiropractic’s Birthday (16 Sept 1895) which is closely followed by World Spine Day on 16 October. To celebrate these two milestone events in Chiropractic, just for fun, we thought we would put together an A-Z of Chiropractic. While some of these words, phrases or terms may not relate only to Chiropractic care, they are ones that we see and hear regularly in our practice.
A
Adaptability: Health is determined by the ability of your mind-body to adapt to its environment (both internal and external). Something that is vitally important in the ever-changing world we live in.
Adjustment: The basic premise behind a Chiropractic adjustment is to detect, analyse and correct misalignments of the spine (called subluxations) to remove interference to the nervous system and improve health. You will sometimes hear people refer to this as a Chiropractic manipulation however we prefer the term adjustment as what Chiropractors do is more specific.
Advanced BioStructural Correction: There are over 200 named techniques within the Chiropractic profession. Advanced BioStructural Correction or ABC, is just one of them and is the one that our Chiropractors mainly utilise. To find out more about it, click here.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Also known as Bechterew’s disease, it is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects the spine and large joints. Symptoms include hip pain, stiff back / reduced flexibility, hunched-forward posture. Pain in the back and joints is also common.
Arthritis: Is inflammation of one or more joints which causes pain or stiffness that often worsens over time. Symptoms include pain, swelling, reduced range of motion and stiffness. There are many different types of arthritis with varying causes.
Atlas: This is the name given to the first cervical vertebra (C1) of the spine and is located in the neck. It gets its name from Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the weight of the world, it supports the entire head.
Autonomic Nervous System: The autonomic nervous system controls the function of our organs and glands. It can be divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. It is part of the peripheral nervous system and works automatically (autonomously), without you having to make any conscious effort. It regulates certain body processes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal.
B
Back: This is a fairly obvious one. Most people know Chiropractors as the ‘Back Doctor’ but we know that Chiropractic care, while it’s focus is on removing interference to the spine, is about way more than just the back.
Bodywork: Is a broad term used to describe body-centred therapies performed by a qualified practitioner to help improve health and well-being.
Bulging Disc: Bulging discs occur when the outer shell of the spongy discs between the vertebrae becomes weaker allowing to become compressed and bulge out or flatten. Symptoms of a bulging disc include pain in the neck, shoulder, arm, chest back or legs, leading to numbness, tingling or weakness in the arms or legs. It can often also cause sciatic pain.
Bursitis: Bursitis is the term used to describe the inflammation of a small fluid filled sacs (bursae) that act as cushions at the joint. It often occurs at joints that perform frequent repetitive motion e.g. knees, shoulders, elbows and hips. Symptoms of bursitis include pain swelling and stiffness.
C
Central Nervous System: The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the body. It consists of a large nerve running from the superior (higher) to the inferior (lower), with the superior end enlarged into the brain. Not all animals with a central nervous system have a brain, although the large majority do.
Cervical Spine (Neck): The cervical spine is located between the cranium (head) and the thoracic spine (mid-back). It consists of 7 vertebrae, two of which are given very distinct names: The first cervical vertebra (C1) is known as the atlas. The second cervical vertebra (C2) is known as the axis.
Chronic Pain: Chronic pain is when your body continues to hurt weeks, months or even years after an injury or illness has healed or gone away. It is classed as chronic pain when it lasts longer than six months.
Coccyx (Tailbone): The coccyx is the small triangular bone at the base of the spine often referred to as the tailbone. It is made up of three to five fused vertebrae. Pain in the coccyx is referred to as coccydynia.
Compressed Nerve: A compressed nerve or pinched nerve occurs when too much pressure is applied to a nerve where it branches out from the spine. The most common symptoms of a compressed nerve are pain in the area of compression, such as the neck or low back, radiating pain, such as sciatica or radicular pain, numbness or tingling, ‘pins and needles’ or a burning sensation, weakness. Sometimes symptoms can worsen when trying certain movements like turning your head.
Cranial-Sacral Therapy: Sometimes referred to as craniosacral therapy, it is a type of bodywork. It is one of the many named techniques often used by Chiropractors.
D
Doctor Within: Within each of us lies what Chiropractic has termed the “Doctor Within”. Simply put, the Doctor Within your body is the doctor who should get all the credit for the healing that takes place within your body. When you embrace the idea of the doctor within, you realise that your body has the innate ability to heal itself. All healing is done within the body, for the body and by the body.
Degenerative Disc Disease: DDD is not actually a disease, but rather a term that refers to weakening of one or more vertebral discs which normally act as a cushion between the vertebrae. It is mostly associated with ageing or wear-and-tear and may or may not cause pain.
Discectomy: A surgical procedure to remove abnormal disc material that is pressing on the nerve root or the spinal cord. The procedure involves the removal of a portion of an intervertebral disc. Surgery should only be considered after conservative options have been exhausted.
Degenerative Arthritis: A term synonymous with osteoarthritis that involved the chronic breakdown of cartilage in the joints leading to painful joint inflammation. The most common symptoms are joint pain in the hands, neck, lower back, knees or hips.
E
Endometriosis: A gynaecological disorder in which tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside the uterus. With endometriosis, the tissue can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes or the intestines. The most common symptoms are pain and menstrual irregularities.
F
Facet Joints: The joints above and below each intervertebral disc, allowing the spine the bend. The paired joints located in the posterior portion of the vertebral bodies connecting the spine. These joints are part of the stabilising mechanism for the spine. Degeneration to these joints is called Facet Joint Syndrome.
Fascia: The thin casing of connective tissue that surrounds and holds every organ, blood vessel, bone, nerve fibre and muscle in place. Fascia has nerves which make it almost as sensitive as skin. Inflammation of the fascia is known as fasciitis.
Fertility: Even if you are not trying to conceive, Chiropractic care can help to free up any interference to the nerves that lead to your reproductive organs.
Fibromyalgia: A term used to describe widespread muscle pain and tenderness. It is often accompanied by fatigue, altered sleep, memory and mood. It is the second most common condition affecting bones and muscles yet is often misdiagnosed and misunderstood. Other names for this include fibrositis and fibromyositis.
Foraminal Stenosis: The foramina are the openings on each side of the vertebrae through which the spinal nerves pass. Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing or tightening of the openings between the bones in the spine that causes pressure on the nerve. Symptoms relating to this include severe back pain, weakness in the arms and legs, numbness and tingling.
G
Goals: Our Chiropractors work with you to help you achieve your health goals. They give their best recommendations for care based on your history, examinations and personal health goals.
H
Herniated Disc: A disc that protrudes from its normal position between two vertebrae, due to an injury to the annulus (outer area of the disc); frequently associated with the nucleus of the disc (inner disc) oozing out of the centre of the disc. Symptoms may occur when the herniation compresses the nerve. Also called a ruptured disc or slipped disc.
High Blood Pressure or Hypertension: A condition where the force of the blood flowing through your blood vessels is constantly too high. Often referred to as the silent killer, as it has no obvious symptoms until the heart, arteries and other organs begin to fail. High blood pressure can put you at risk of heart disease, heart failure or stroke.
Hypothalamus: The part of our brain that controls all of the autonomic functions of the body, including breathing, heartbeat, digestion, sleep and the complex functions of the endocrine system. One of its main functions is homeostasis; maintaining the body’s status quo. The effectiveness of the hypothalamus is directly proportional to the functional capability of the nervous system to send and receive nerve messages and especially to maintain the integrity of those nerve messages as they travel along the spinal cord.
I
Inflammation: Part of your immune system’s natural response to heal an injury or fight an infection or toxins. Often associated with redness, heat, swelling, pain and loss of function. This process destroys tissues but is also associated with the repair and healing of body structures.
Insulin: An essential hormone made inside of your pancreas which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. If the insulin balance is off, it can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An increasingly common chronic condition that affects the large intestine. The cause of IBS isn’t well understood, and diagnosis is made based on symptoms. Symptoms include abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, gas, diarrhoea and/or constipation.
J
Jargon: Doctors like to use big fancy (often Latin) words and Chiropractors are no different. Hopefully this list will help to clear up some of that jargon and help you to understand these terms better.
K
Kyphosis: The normal curve of the thoracic spine. This term also describes an excess curvature of the thoracic spine called a “Dowager’s Hump.” This is commonly observed in people with osteoporosis but is becoming more common in younger people with the excessive use of electronic devices.
L
Lumbar Spine (Low-Back): The lower five weight bearing vertebrae that are located between the thoracic vertebrae and the sacrum.
Laminectomy: A surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the lamina (the roof of the spinal canal). It is a major spine operation that can help ease the pressure in the spinal cord or the nerve root. Residual scar tissue as a result of this surgery can cause postlaminectomy syndrome. This surgery should only be considered if other conservative options (like Chiropractic care) have been exhausted.
Ligament: Ligaments are bands of tough elastic tissue around your joints. They connect bone to bone, give your joints support, and limit their movement. You have ligaments around your knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders, and other joints. Stretching or tearing them can make your joints unstable. Common ligament injuries you may have heard of are torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL), torn Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL), temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, sprained ankle, plantar fasciitis / runners heel, acromioclavicular (AC) separation / shoulder separation.
Lordosis: Lordosis is a normal inward curve of the spine. This term is also used to describe the excessive inward curve that affects the neck or lower back. While some lordosis is normal, excessive lordosis can cause health challenges. You may also hear it being called hyperlordosis, lumbar lordosis or swayback.
Low Back Pain: Also known as lumbago. There could be many causes of low back pain improper lifting, poor posture, lack of regular movement, nerve irritation, fracture or disease. Pain is your body’s way of telling you that something isn’t right and should warrant further investigation.
M
Meningeal Release: One of the big stretches that are part of the ABC™ technique protocol. The more adhesions and scar tissue in the meninges – the connective tissue covering the brain and spinal cord – the greater the tension on the brain and spinal cord. The meningeal release is designed to release scar tissue and adhesion of the meninges deep within the spine.
Manipulation: Spinal manipulation, spinal manipulative therapy or manual therapy combines moving and jolting joints, massage, exercises and physical therapy. This is not to be confused with a Chiropractic adjustment, as explained above.
Metabolism: Metabolism describes all the chemical processes that go on continuously inside your body to keep you alive and your organs functioning normally, such as breathing, repairing cells and digesting food.
Muscle Spasm: Involuntary contractions of a muscle, typically harmless and temporary, but can be painful.
Muscle Tension: Muscle tension refers to the condition in which muscles of the body remain semi-contracted for an extended period. Muscle tension is typically caused by the physiological effects of stress and can lead to episodes of back pain.
Remember, muscles don’t think for themselves, they are controlled by your nervous system.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Myofascial pain syndrome is chronic pain disorder in which pressure on sensitive points in the muscles causes pain in seemingly unrelated body parts. The syndrome often happens after repeated injury or muscle overuse. Symptoms include persistent pain or a tender muscle knot.
Myofascial Release: A bodywork technique sometimes utilised by Chiropractors to relieve the symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome.
N
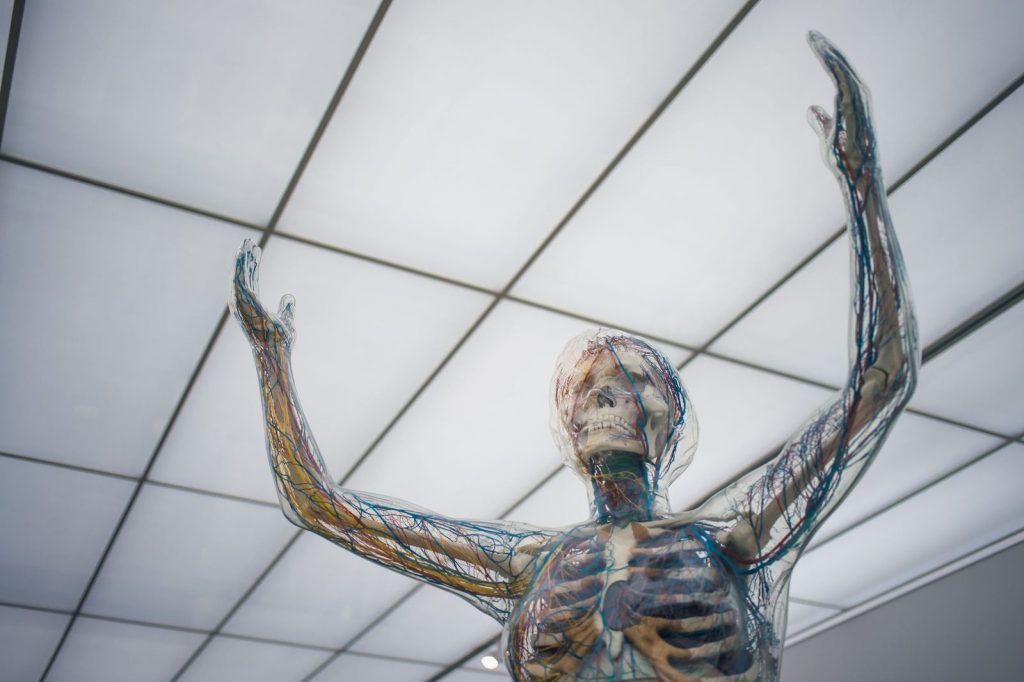

Nervous System: The complex, sophisticated system that controls and regulates all functions in the body. It’s your body’s command centre, originating at your brain. The nervous system is made up of two major divisions: Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System.
Nerve: A glistening white cordlike bundle of fibres, surrounded by a sheath, that connects the nervous system with other parts of the body.
Nerve Block: Also knows as a neural blockade, is a procedure that are used to prevent or manage different types of pain. Often done as an injection of medicine that block pain from specific nerves. Not only can they be used for pain relief but also used in surgery to achieve a complete loss of feeling.
Neuromuscularskeletal: The (neuro)musculoskeletal system comprises the bones of the skeleton, the joints at which movement occurs, the muscles that move them and the nerves that stimulate the muscles. The central nervous system must also be included as it is the coordinator of all of your body’s functions. The skeletal and muscular systems are interconnected through joints and connective tissue. Dysfunction in one part will ultimately affect adjacent parts and may also have a broader effect through postural or gait adaptations.
O
Osteoporosis: Meaning ‘porous bone’ it is a disease characterised by the loss of bone density, resulting in weakness and brittleness. The body constantly absorbs and replaces bone tissue. With osteoporosis, new bone creation doesn’t keep up with old bone removal.
Many people have no symptoms until they have a bone fracture. It most commonly affects the spinal vertebrae, wrists and hips.
Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis that occurs when the flexible tissue (cartilage) at the ends of bones wears down. Also called degenerative joint disease, the wearing down of the cartilage occurs gradually and worsens over time. It occurs most frequently in the hands, hips and knees and pain in these areas, the neck and lower back are the most common symptoms.
Osteophytes: Osteophytes are bony lumps (bone spurs) that grow on the bones of the spine or around the joints. They often form next to joints affected by osteoarthritis. Osteophytes can grow from any bone, but they’re most often found in the neck, shoulder, knee, lower back, fingers or big toe, foot or heel. Osteophytes don’t always cause symptoms but some people can experience pain and stiffness in the back, pins and needles, numbness or weakness in the arms, shoulder injuries, painful arthritis and pain in the legs.
Orthopedic Surgeon: A surgeon who specialises in the musculoskeletal system. There are seven main sub-specialities of orthopedic medicine: spine surgery, hand surgery, sports medicine, total joint replacement (hip and knee), pediatric orthopedics, foot and ankle (podiatry), and orthopedic oncology.
P
Pain: Chiropractors are best known for but not limited to assisting with back pain, neck pain, headaches and injuries.
Piriformis Syndrome: a condition in which the piriformis muscle, located in the buttock region, spasms and causes buttock pain. The piriformis muscle can also irritate the nearby sciatic nerve and cause pain, numbness and tingling along the back of the leg and into the foot (similar to sciatic pain).
Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is inflammation of the thick band of tissue (also called a fascia) at the bottom of your foot that runs from your heel to your toes. It causes pain in the heel that is usually worse in the morning or after extended periods of rest. Doctors once thought bony growths called heel spurs brought on the pain, now they believe that heel spurs are the result of, not the cause of, plantar fasciitis
Parasympathetic nervous system: The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system and helps up to recover from stress. It is responsible for controlling functions when a person is at rest. It is also referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
Q
Questions: Click here for Frequently Asked Questions about Chiropractic care.
R
Repetitive Strain Injury: A term used to describe damage and pain caused by repetitive movement and overuse. Also known as overuse injury, work-related upper limb disorder or non-specific upper limb pain. Repetitive strain injury impacts muscles, nerves, ligaments and tendons. These types of injuries can be caused by improper technique or overuse. The elderly are most commonly affected. Symptoms include tenderness, stiffness or tingling in the affected area.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An auto-immune and inflammatory disease where the body’s own immune system attacks its own tissue, including joints. It affects the facet joints in the spine as well as other joints in the body including the hands, elbows, shoulders, fingers and toes, causing painful swelling. In severe cases, it attacks internal organs. Over long periods of time, the inflammation associated with RA can cause bone erosion and joint deformity.
Ruptured Disc: See Herniated Disc above.
S
Subluxation: A misalignment in the spine. Subluxations can create pressure or irritation on the nerves in your spine and cause a wide variety of symptoms throughout your body. When a misalignment puts pressure on a nerve in your spine, the nerve flow is interrupted which can affect the function of other systems or organs in your body.
Sciatic Nerve / Sciatica: A major nerve extending from the lower end of the spinal cord down the back of the thigh and dividing above the knee joint. It is the nerve with the largest diameter in the human body. Click here to read more about Sciatica.
Scoliosis: Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that most often is diagnosed in adolescents. While scoliosis can occur in people with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most childhood scoliosis is unknown. Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some curves worsen as children grow. Click here to read more about Scoliosis.
Slipped Disc: See herniated disc above.
Spina Bifida: A birth defect in which a developing baby’s spinal cord fails to develop properly in the womb. It is a type of neural tube defect (NTD). Symptoms can sometimes be seen on the skin above the spinal defect. They include an abnormal tuft of hair, a birthmark or protruding spinal cord tissue.
Spinal Canal: Spinal canal refers to the hollow passage formed by the foramen of the vertebrae through which the spinal cord runs. The spinal canal is filled with cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the nerves. The canal originates at the base of the skull and ends at the sacrum.
Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS).
Spinal Fracture: There are many different types of spinal fractures: Compression, Burst, Flexion-distraction, and Fracture-dislocation. Other terms your doctor may use to describe a fracture include stable, unstable, minor, and/or major. Spinal fractures are different than a broken arm or leg. A fracture or dislocation of a vertebra can cause bone fragments to pinch and damage the spinal nerves or spinal cord. Most spinal fractures occur from car accidents, falls, gunshot, or sports.
Spinal Fusion: A neurosurgical or orthopaedic surgical technique used to permanently connect two or more vertebrae in your spine. The procedure can be performed at any level of the spine and prevents any movement between the fused vertebrae. It is also known as spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis. This surgery should only be considered if all other options have been exhausted.
Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine, which eventually results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms of spinal stenosis vary widely from person to person and range from no symptoms to pain in the back or neck and numbness, tingling and weakness in the arms and/or legs, muscle weakness, and impaired bladder or bowel control.
Sympathetic Nervous System: The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system. It directs the body’s rapid involuntary response to dangerous or stressful situations. It is also referred to as the “fight or flight” system.
T
Thoracic Spine (Mid-Back): The thoracic spine is the longest region of the spine, and by some measures it is also the most complex. There are twelve vertebrae that connects the cervical spine and the lumbar spine. It is the only spinal region attached to the ribcage.
Tendon: Located at each end of a muscle and attach muscle to bone. Tendons are found throughout the body, from the head and neck all the way down to the feet. Most tendon injuries occur near joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, knee, and ankle.
Tennis Elbow: An irritation of the tissue connecting the forearm muscle to the elbow that causes pain around the outside of the elbow. It can be caused by overuse or repetitive wrist and arm motions.
U
Under-recognised: Chiropractic care is hugely under-recognised and often misunderstood. To find out more about what Chiropractic care is, click here for a short video.
V
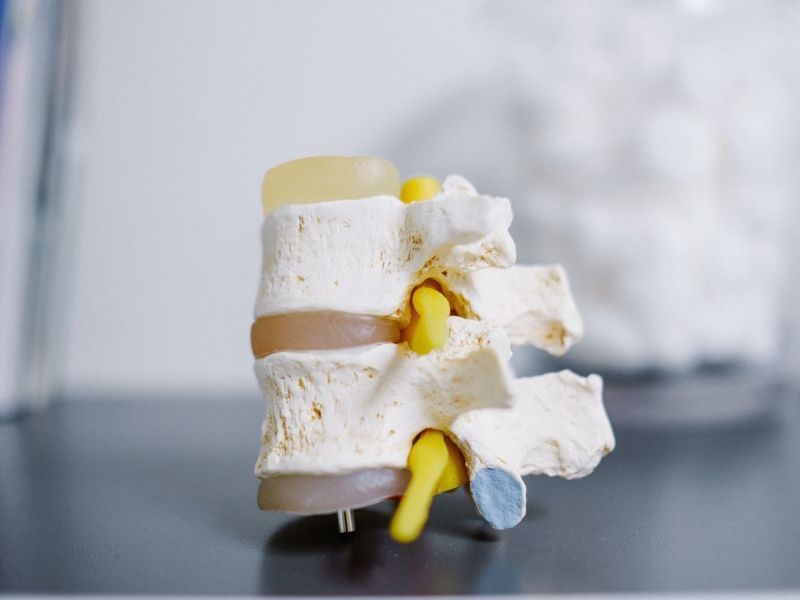

Vertebrae: The 33 individual bones that interlock with each other and make up the ‘backbone’ of the skeleton commonly known as the spine. The vertebrae are numbered and divided into regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx. Only the top 24 cylindrical segments of bone are moveable; the vertebrae of the sacrum and coccyx are fused.
W
Whiplash: An injury to the cervical spine that occurs from rapid hyper-flexion, hyper-extension and compression movements, such as a car accident. Read more about whiplash here.
X
X-ray: X-ray is a diagnostic tool that produces images of the structure of your body. The images show the parts of your body in different shades of black and white. The most familiar use of x-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but x-rays are also used in other ways.
Read more about X-ray imaging here.
Y
Why do people go to a Chiropractor? There are many reasons why people visit a Chiropractor. Whether you are looking for relief and stabilisation, correction and regeneration, prevention, or optimisation and wellness, our team are here to assist you on your journey.
Z
Zzzzzz (Sleep): In a recent study of 221 Chiropractic patients, one third reported immediate effect on their sleep after a Chiropractic adjustment. From this group a massive 98% recorded improved results with Chiropractic versus those whose sleep patterns did not get better. Pain (acute and chronic) is a major cause of sleep disturbances, be it neck, back, shoulder pain or headaches, ALL of which chiropractic has been shown to be able to help.
We do not claim that Chiropractic care treats or cures any of the conditions in this article.
What Chiropractors do is care for you by removing subluxations and allowing your body to function optimally.
The Chiropractic philosophy understands that the power that made the body, heals the body and while Chiropractors can help you to remove those subluxations, it is your own body that does the healing.
Peak Chiropractic Centre located in Claremont are family-friendly chiropractors focused on relieving aches, pains and posture correction. We offer in-house X-Ray facilities.

